Casting deformation remains one of the most prevalent quality challenges in foundry operations. A critical pain point arises when parts fail final inspection after undergoing 12-18 production stages, resulting in costly rework and delayed deliveries. This analysis systematically examines the metallurgical and procedural origins of dimensional instability while proposing actionable countermeasures to align outputs with design specifications.
Deformation manifests as measurable deviations from intended geometries, including but not limited to:
-
Axial bending (≥0.5mm/m linear distortion)
-
Planar warping (surface flatness exceeding ±1.2mm)
-
Radial distortion (ovality >0.8% of nominal diameter)
-
Asymmetric wall thickness (variations surpassing ±15% nominal value)
These anomalies are classified as macro-deformations when affecting overall part architecture (>3% dimensional shift) or micro-deformations for localized discrepancies (0.5-3% deviation). Crucially, any deviation exceeding ±0.25mm from GD&T requirements constitutes non-conforming deformation per ASTM A802 standards.

Patterns of Casting Deformation
Through empirical observation, a clear deformation trend emerges: thick-walled sections typically exhibit inward concavity (dishing effect), while thin-walled components predominantly demonstrate outward convexity (dome effect). This fundamental behavior stems from differential solidification rates, where thicker sections experience prolonged thermal contraction, creating inward stress vectors.
Consequences of Casting Deformation
Dimensional instability precipitates three critical production failures:
-
Non-compliance with specifications – Deviations exceeding ±0.5mm routinely violate blueprint tolerances
-
Downstream machining interference – Warped surfaces induce fixture misalignment (typical 0.1-0.3mm positioning error)
-
Material viability compromise – Severe distortion consumes >30% of machining allowances, with 12-18% of affected castings becoming unrecoverable scrap. Surface irregularities (Ra >6.3μm) further exacerbate tool wear, increasing machining costs by 15-22%.
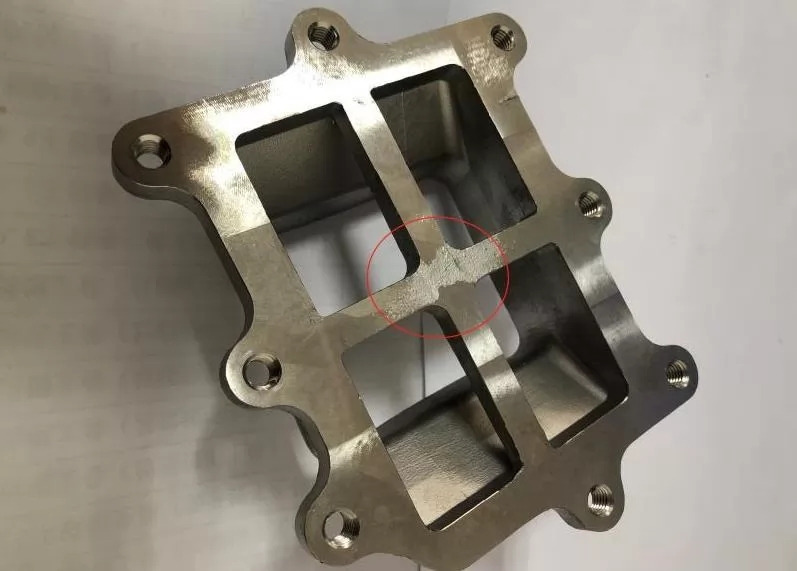

This demonstrates that effective management of casting deformation is crucial for product quality. While casting stress remains the primary driver of deformation, it’s important to recognize that we can only minimize these stresses rather than eliminate them entirely. Implementing targeted stress-reduction measures represents the most practical approach to preventing dimensional instability in castings.
Root Causes of Casting Deformation
-
Wax Pattern Distortion
During production, wax patterns undergo handling and positioning processes where improper mold installation or premature handling (before complete cooling) frequently leads to deformation. Even post-extraction placement significantly impacts pattern integrity, with improper support causing up to 0.3-0.5mm dimensional deviation in final castings. -
Structural Design-Induced Deformation
Products with non-uniform wall thickness exhibit differential shrinkage during both wax pattern creation and metal pouring. Thick sections (typically >8mm) experience 30-50% greater contraction than thin walls (<4mm), resulting in characteristic depressions and warpage. This phenomenon accounts for approximately 40% of all casting deformation cases. -
Improper Shell Handling Post-Pouring
The critical period immediately after pouring (when castings remain at 600-800°C) demands strict handling protocols. Stacking or improper support during this phase introduces external forces to the semi-solid casting, while the material’s unstable mechanical properties (particularly between solidus and liquidus temperatures) make it exceptionally vulnerable to deformation. Uncontrolled cooling during this stage causes up to 60% of avoidable

. Vibration-Induced Deformation During Shell Removal
The shell removal process presents critical deformation risks when operators employ excessive vibration parameters or improper techniques. High-frequency vibratory forces (typically 50-100Hz) can induce resonant distortion in partially constrained castings, particularly affecting:
-
Thin-walled geometries (<3mm) with low structural rigidity
-
Complex assemblies with unsupported spans >150mm
-
High-aspect-ratio components (length:thickness ratios exceeding 8:1)
Best practice requires:
-
Controlled vibration intensity (≤0.5mm amplitude)
-
Sequential multi-axis vibration for uniform stress distribution
-
Specialized fixtures to support vulnerable features during debonding
-
Real-time monitoring with laser displacement sensors for high-value castings

5. Heat Treatment-Induced Deformation
The thermal processing stage introduces two primary deformation mechanisms:
-
Material softening – Castings lose 40-60% of their room-temperature strength when heated to 650-950°C, becoming susceptible to gravity-induced sagging (typically 0.1-0.3mm/m deflection)
-
Stress relief distortion – Residual stresses from casting processes release abruptly during heat treatment, causing unpredictable dimensional shifts of up to 1.2% of nominal dimensions
These effects compound to create permanent geometric deviations exceeding ±0.8mm in critical dimensions, particularly affecting:
-
Long-span components (>500mm)
-
Asymmetric geometries
-
Thin-walled structures (<5mm)
6. Wax Assembly Welding Distortion
Complex gating systems with multiple feeders (≥3 risers) exhibit particular vulnerability to:
-
Gate misalignment – Welding forces can induce 2-5° angular deviation between supposedly coaxial runners
-
Structural warpage – Localized heating during welding creates thermal gradients causing 0.4-1.2mm/m bowing in cluster assemblies
This primarily affects:
-
Multi-cavity molds with intricate runner networks
-
Components requiring precision-matched parting lines
-
Large-diameter annular castings (>300mm OD)
7. Shell Coating Process Deformation
Improper shell-building techniques introduce dimensional instability through:
-
Slurry expansion – Uncontrolled binder ratios cause 0.15-0.25% linear growth during drying
-
Differential drying – Non-uniform drying rates create internal stresses leading to 0.3-0.6mm warpage
-
Handling stresses – Premature handling of green shells (<12hr cure time) induces permanent deformation
Critical control points include:
-
Maintaining 45-55% binder solids content
-
Controlled drying environments (22±2°C, 50±5% RH)
-
Minimum 24hr inter-coat curing for structural shells
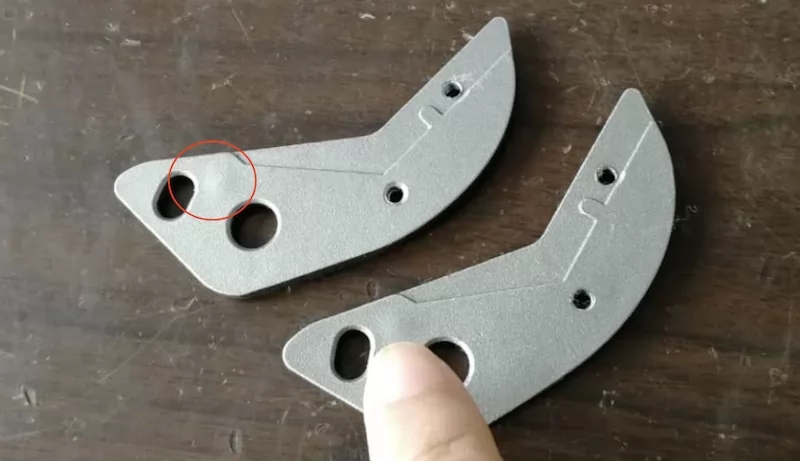

8. Deformation caused by subsequent processes.
In the post-treatment process, excessive shot peening and a large number of product stacking will lead to casting deformation.

How to Prevent Casting Deformation
-
Optimized Product Structure Design
-
Implement uniform wall thickness principles (recommended thickness variation <30%)
-
Conduct comprehensive DFM (Design for Manufacturing) analysis during prototyping
-
Utilize simulation software to predict and mitigate deformation risks before tooling
-
Deformation Compensation Engineering
-
Our China Metal Castings system employs:
-
Dimensional mapping of wax patterns vs. final castings
-
Statistical process control with >500 data points per product family
-
Iterative die correction algorithms based on historical deformation patterns
-
-
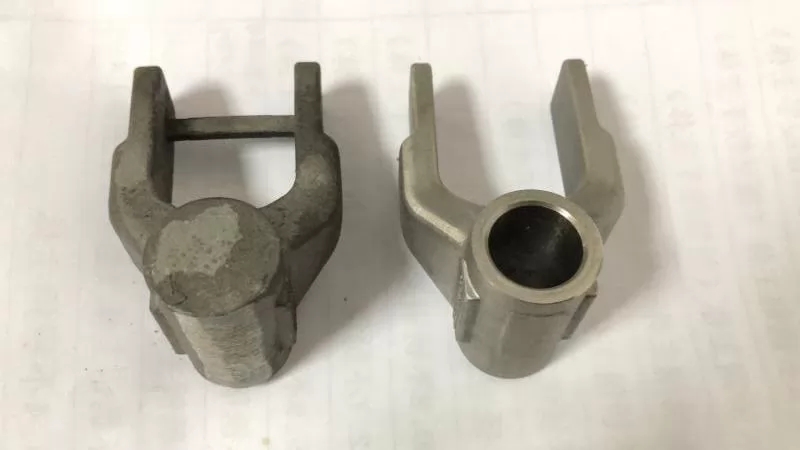
Structural Reinforcement Techniques
For open-frame castings:
-
Apply temporary process ribs (typically 3-5mm thick) at strategic locations
-
Implement graduated rib tapering to prevent stress concentration
-
Achieve 60-75% reduction in warpage for box-type structures

-
Machining Allowance Strategy
When structural modification is impossible:
-
Apply variable machining allowances (thick sections: +1.5mm, thin walls: +2.2mm)
-
Implement datum-driven machining protocols
-
Maintain minimum 0.8mm finish allowance on all critical surfaces
-
Advanced Wax Pattern Control
Critical control measures:
-
Precision cooling systems (20°C water spray ±2°C control)
-
Customized support fixtures for complex geometries
-
Standard block reference system (accuracy: ±0.05mm)
-
Real-time laser scanning verification during cooling
-
Post-Casting Process Optimization
-
Automated handling systems with vacuum-assisted gripping
-
Stress-relief annealing before machining (650°C for steel, 350°C for aluminum)
-
Dedicated inspection fixtures for intermediate process verification
How to correct the deformation of castings
Methods for Correcting Casting Deformation
-
Cold Correction Technique
-
Applicable for:
-
Small-to-medium deformations (typically <3mm deviation)
-
High manganese steel castings (mandated by material properties)
-
-
Implementation methods:
-
Manual hammering (for localized corrections)
-
Hydraulic/pneumatic presses (50-200 ton capacity)
-
Specialized straightening jigs (precision ±0.1mm)
-
-
Limitations:
-
≤40% success rate for standard carbon steel castings
-
Risk of micro-cracking in brittle materials
-
-
Thermal Correction Methods
Two distinct temperature regimes:
High-Temperature Correction (Austenitizing Range)
-
Temperature range: 850-1100°C (material dependent)
-
Advantages:
-
70-90% correction efficiency
-
Complete stress relief
-
-
Challenges:
-
Requires skilled operators (≥5 years experience)
-
Potential grain growth concerns
-
Low-Temperature Correction (Stress-Relief Range)
-
Temperature range: 480-650°C
-
Benefits:
-
85-95% success rate
-
Minimal metallurgical impact
-
-
Considerations:
-
Extended processing time (2-4 hours)
-
Requires precise temperature control (±10°C)
-
Critical Implementation Guidelines
-
Conduct thorough DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Analysis) during process planning
-
Prioritize correction method based on:
-
Material grade (carbon steel vs. alloy steel)
-
Section thickness (critical for heat penetration)
-
Dimensional tolerance class (IT12-IT14)
-
-
Implement laser scanning verification post-correction
-
Maintain detailed correction logs for process optimization
Preventive Engineering Approach
Proactive measures significantly reduce correction needs:
-
Simulation-driven gating design
-
Controlled cooling protocols
-
Stress-relief annealing cycles
-
Automated dimensional monitoring