
The Complete Guide to Die Casting:
Introduction to Die Casting Technology
Die casting stands as one of the most efficient and precise metal forming processes available to modern manufacturers. This high-pressure metal casting method transforms molten metal into complex, net-shaped components with exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface finish. As a cornerstone manufacturing process across industries from automotive to consumer electronics, die casting enables mass production of metal parts with remarkable consistency and cost-effectiveness.
China Metal Castings has established itself as a professional die casting manufacturer in China, specializing in high-quality aluminum, zinc, and magnesium die cast components for global industries. With advanced manufacturing facilities and decades of expertise, we deliver precision die cast parts that meet the most stringent quality standards while optimizing production efficiency.
This comprehensive guide provides manufacturing engineers, product designers, and procurement specialists with an in-depth understanding of:
- The fundamental principles of die casting technology
- Detailed process variations and methodologies
- Material selection guidelines for optimal performance
- Design considerations for die cast components
- Industry-specific applications and case studies
- Comparative analysis with alternative manufacturing methods
- How to select the ideal die casting partner
1: Understanding Die Casting Fundamentals
1.1 What is Die Casting?

Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into reusable steel molds called dies. The process is particularly valued for:
- High production rates – Capable of producing hundreds to thousands of parts per hour
- Exceptional dimensional accuracy – Typical tolerances of ±0.1mm for the first inch
- Superior surface finishes – As-cast surface finishes of 1-2μm Ra achievable
- Complex geometries – Can produce intricate shapes with thin walls (as thin as 0.5mm)
- Material efficiency – Near-net shape production minimizes machining waste
1.2 Historical Development of Die Casting
The origins of die casting trace back to the mid-19th century when the process was first developed for producing movable type for printing presses. Key milestones include:
- 1849 – First patent for a small hand-operated machine for casting printing type
- 1885 – Otto Mergenthaler’s Linotype machine revolutionized printing with die cast type
- Early 1900s – Adoption by the growing automotive industry for components
- 1920s – Development of aluminum and zinc alloys expanded applications
- 1940s – Wartime production drove advancements in high-volume manufacturing
- Modern Era – Computer-controlled machines and advanced alloys continue to push boundaries
1.3 Why Choose Die Casting Over Other Processes?
Compared to alternative manufacturing methods, die casting offers distinct advantages:
| Factor | Die Casting | Sand Casting | Injection Molding | Forging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Very High | Low | Very High | Medium |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Excellent | Fair | Excellent | Good |
| Surface Finish | Excellent | Rough | Excellent | Good |
| Wall Thickness | 0.5-5mm | 3mm+ | 0.5-4mm | 3mm+ |
| Tooling Cost | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Material Options | Non-ferrous | All metals | Plastics | All metals |
2: The Die Casting Process Step-by-Step
2.1 Comprehensive Process Overview
The die casting process consists of five primary stages, each critical to producing high-quality components:
Stage 1: Mold Preparation and Design
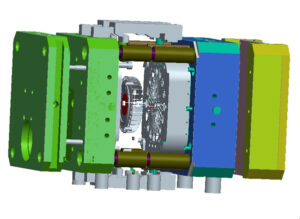
Die molds are precision-engineered from high-grade tool steels (typically H13 or P20) with hardness ratings of 46-50 HRC. Mold design considerations include:
- Single vs. multi-cavity configurations
- Gating and runner systems
- Cooling channel placement
- Ejector pin locations
- Draft angles (typically 1-3°)
- Surface treatments (nitriding, chrome plating)
At China Metal Castings, we utilize advanced simulation software to optimize mold designs before manufacturing, reducing development time and ensuring optimal performance.
Stage 2: Metal Melting and Injection

The injection phase varies significantly between hot chamber and cold chamber systems:
Hot Chamber Process:
- Metal melted in integrated furnace (600-700°C for zinc)
- Gooseneck mechanism injects metal (1000-5000 psi)
- Cycle times as fast as 15-30 seconds
- Limited to lower melting point alloys
Cold Chamber Process:
- External melting (660-750°C for aluminum)
- Ladled into cold chamber
- Higher pressures (1500-25,000 psi)
- Longer cycle times (30-90 seconds)
- Suitable for high-temperature alloys
Stage 3: Solidification and Cooling
Proper cooling is critical for:
- Minimizing porosity
- Preventing shrinkage defects
- Achieving dimensional stability
- Optimizing mechanical properties
Cooling rates typically range from 50-300°C per second depending on alloy and part geometry. China Metal Castings employs advanced cooling channel designs and temperature monitoring systems to ensure consistent results.
Stage 4: Ejection and Trimming
After sufficient solidification:
- Ejector pins (0.5-2mm diameter) release the part
- Trimming removes flash and overflow material
- Automated robotic systems often handle these operations
Stage 5: Finishing and Quality Control

Post-casting operations may include:
- CNC machining for critical features
- Deburring and surface finishing
- Heat treatment (T5, T6, T7)
- Plating, painting, or powder coating
- 100% dimensional inspection
- X-ray and porosity testing
2.2 Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Die Casting
Detailed comparison of the two primary die casting methods:
| Parameter | Hot Chamber | Cold Chamber |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Location | Inside machine | External furnace |
| Pressure Range | 1000-5000 psi | 1500-25,000 psi |
| Injection Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Alloy Compatibility | Zinc, magnesium, low-temp aluminum | Aluminum, copper, high-temp alloys |
| Typical Applications | Small precision parts (gears, connectors) | Large structural components (engine blocks, housings) |
3: Advanced Die Casting Variations
3.1 Gravity Die Casting (Permanent Mold Casting)
- Utilizes gravity feed rather than pressure
- Lower porosity and better mechanical properties
- Slower cycle times than pressure die casting
- Common for automotive components like cylinder heads
3.2 Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC)
- Filling pressure: 0.08-0.1 MPa
- Reduced turbulence and gas entrapment
- Excellent for large, thin-walled parts
- Common in automotive wheel production
3.3 Vacuum Die Casting
- Uses vacuum to remove air from die cavity
- Minimizes porosity by 50-70%
- Improves weldability and heat treatability
- Critical for structural aerospace components
3.4 Squeeze Die Casting
- Combines casting and forging principles
- Applied pressure during solidification
- Near-forged mechanical properties
- Used for high-integrity automotive parts
3.5 Semi-Solid Die Casting (Thixocasting)
- Processes metal in semi-solid state
- Reduced shrinkage and porosity
- Excellent dimensional accuracy
- Growing use in electric vehicle components
4: Material Selection for Die Casting
4.1 Aluminum Alloys

Most Common Alloys:
- A380 (most widely used)
- A383 (improved die filling)
- A360 (high corrosion resistance)
- ADC12 (Japanese standard)
Properties:
- Density: 2.7 g/cm³
- Tensile strength: 220-330 MPa
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good thermal/electrical conductivity
Applications:
- Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission cases
- Electronics: Heat sinks, housings
- Industrial: Pump housings, valves
4.2 Zinc Alloys

Common Alloys:
- Zamak 3 (general purpose)
- Zamak 5 (higher strength)
- ZA-8 (higher aluminum content)
Properties:
- Density: 6.6 g/cm³
- Tensile strength: 280-440 MPa
- Excellent castability
- Superior surface finish capability
Applications:
- Consumer products: Door hardware, zippers
- Automotive: Carburetor parts, brackets
- Electronics: Connectors, shielding
4.3 Magnesium Alloys
Common Alloys:
- AZ91D (most common)
- AM60B (higher ductility)
- AS41B (creep resistant)
Properties:
- Density: 1.8 g/cm³ (lightest structural metal)
- Tensile strength: 230-290 MPa
- Excellent stiffness-to-weight ratio
- Good EMI shielding
Applications:
- Aerospace: Seat frames, gearbox housings
- Automotive: Steering wheels, instrument panels
- Electronics: Laptop cases, camera bodies
4.4 Copper Alloys
Common Alloys:
- Brass (Cu-Zn)
- Bronze (Cu-Sn)
- Beryllium copper
Properties:
- Excellent thermal/electrical conductivity
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Antimicrobial properties
Applications:
- Electrical: Connectors, switchgear
- Plumbing: Valves, fittings
- Marine: Propellers, hardware
5: Design Considerations for Die Cast Parts
5.1 Wall Thickness Design
- Uniformity is critical – Avoid sudden changes
- Typical range: 1.5-4mm for aluminum
- Minimum: 0.5mm for small zinc parts
- Maximum: 6mm for large aluminum parts
5.2 Draft Angles
- Standard: 1-3° per side
- External surfaces: 1-2°
- Internal surfaces: 2-3°
- Deep cavities: Additional draft may be needed
5.3 Rib Design
- Height: Should not exceed 3x adjacent wall thickness
- Thickness: 50-80% of adjacent wall
- Base radius: Equal to rib thickness
- Spacing: Minimum 2x rib thickness
5.4 Boss Design
- Wall thickness: Equal to adjacent walls
- Height: Maximum 2x diameter
- Reinforcement: Gussets at base if needed
- Hole depth: Maximum 2x diameter
5.5 Parting Line Considerations
- Location: Should minimize flash visibility
- Orientation: Affects tooling complexity
- Design: Should allow for proper ejection
6: Industry Applications of Die Casting
6.1 Automotive Industry
- Engine components: Blocks, heads, manifolds
- Transmission parts: Cases, housings
- Structural elements: Crossmembers, brackets
- Exterior trim: Door handles, emblems
Case Study: Aluminum transmission case reduces weight by 40% compared to iron, improving fuel efficiency.
6.2 Aerospace Applications
- Engine components: Compressor housings
- Structural parts: Brackets, fittings
- Interior components: Seat frames
- Avionics housings
Material Focus: Magnesium alloys for weight savings in airframe components.
6.3 Electronics Industry
- Housings: Laptops, tablets, phones
- Heat sinks: CPU coolers
- Connectors: High-speed data transfer
- Shielding: EMI/RFI protection
Trend: Thin-wall die casting for increasingly compact devices.
6.4 Consumer Products
- Power tools: Housings, gears
- Appliances: Housings, handles
- Furniture hardware
- Sporting goods
Example: Zinc die cast golf club heads with precise weight distribution.
6.5 Medical Equipment
- Device housings
- Surgical instruments
- Imaging equipment components
- Dental equipment
Critical Factor: High-integrity casting for sterile environments.
7: Selecting a Die Casting Partner
7.1 Key Selection Criteria
- Technical capabilities: Alloys, sizes, tolerances
- Quality certifications: ISO 9001, IATF 16949
- Engineering support: DFM analysis
- Production capacity: Volume capabilities
- Secondary services: Machining, finishing
7.2 China Metal Castings’ Capabilities
As a professional die casting manufacturer in China, we offer:
- Alloys: Aluminum, zinc, magnesium
- Processes: High pressure, low pressure, vacuum
- Part size: 10g to 50kg
- Tolerances: ±0.05mm for critical dimensions
- Finishes: As-cast to mirror polish
- Certifications: ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 14001
7.3 The Partnering Process
- Design consultation: DFM analysis
- Prototyping: Rapid tooling options
- Testing: Material and performance validation
- Production: High-volume manufacturing
- Delivery: Global logistics support
8: Future Trends in Die Casting
8.1 Industry 4.0 Integration
- Smart sensors for real-time process monitoring
- Predictive maintenance for tooling
- AI-driven process optimization
- Digital twin technology
8.2 Advanced Materials Development
- High-strength aluminum alloys
- Heat-resistant magnesium alloys
- Nano-composite materials
- Recyclable alloy systems
8.3 Sustainability Initiatives
- Closed-loop water systems
- Energy-efficient melting technologies
- Scrap recycling programs
- Reduced-emission processes
8.4 Electric Vehicle Revolution
- Large structural battery housings
- Integrated motor components
- Lightweight structural parts
- High-conductivity thermal management
Conclusion
Die casting remains one of the most versatile and cost-effective manufacturing processes for high-volume metal component production. From its ability to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances to its compatibility with a range of high-performance alloys, die casting continues to evolve to meet the demands of modern industry.
For organizations seeking a professional die casting manufacturer in China, China Metal Castings offers comprehensive solutions combining advanced technology, engineering expertise, and quality-focused manufacturing. Our capabilities span from initial design consultation through high-volume production, ensuring optimal results for every application.
As manufacturing challenges grow increasingly complex, partnering with an experienced die casting specialist becomes essential to achieving product success in today’s competitive markets. Contact China Metal Castings today to discuss how our die casting solutions can bring your designs to life with precision, efficiency, and quality.
More professional information about Die castings, please check from wikipedia.



