Design of Die Casting Die for Aluminum Alloy Shell
This article first analyzes the structure and die-casting process of the aluminum alloy shell, and uses UG software to complete the design of the aluminum alloy shell die-casting mold. Proved by practice, the designed die-casting is reasonable, the surface of the obtained castings is smooth and clean, and the product quality meets the requirements.
Analysis of the structure and process of die-casting parts of aluminum alloy rear shell
1.1 Die casting structure It can be seen from Figure 1 that the structure of the rear shell stuffy cover casting is relatively simple, the casting wall thickness is basically uniform, there are two casting holes, but because the wall of the casting hole is slightly thicker, hot spots are easy to appear , The overall wall thickness of the die-casting is relatively uniform. When choosing the wall thickness, a variety of factors should be considered: die-casting structure, material properties, and the designed die-casting process. Only thin-walled or uniform wall thicknesses can meet all aspects. need.
1.2 The minimum wall thickness of the outer edge of the casting. Good casting forming conditions require a certain outer edge wall thickness. The relationship between the edge wall thickness s and the depth h is s≥(1/4~1/3)hmm. When h<4.5mm, then s≥1.5mm.
1.3 Die-casting material The material of the die-casting is die-cast aluminum alloy, its grade is YZAlSi9Cu4, the tensile strength is 240MPa, the Brinell hardness is 85HBS, and the average shrinkage rate is 0.6%. The selected alloy results in good casting properties and is particularly suitable for die casting.
1.4 Casting fillet radius In order to make the molten metal flow more smoothly and easily discharge the gas, the structure is designed to use cast fillets, and the use of fillets to replace the sharp corners of the structure can also avoid cracks. The radius of the rounded corners of the designed structure depends on the wall thickness of the structure, and the range is generally 0.5 to 1 mm.
1.5 The drafting angle should be selected by comprehensive consideration of many factors: casting geometry (depth, wall thickness, cavity or core surface), roughness, processing grain direction, etc. Taking into account the above factors, the design of the shell demolding slope of the casting: α=30′ on the outer surface, and β=1° on the inner surface.
Die casting process parameter design
2.1 Die-casting machine selection When choosing a die-casting machine, the clamping force must be determined first. The clamping force has two functions: one is used to balance the back pressure to achieve the purpose of locking the parting surface; the other is to prevent splashing molten metal to achieve the purpose of achieving the target dimensional accuracy. There is no partial expansion force in the designed casting, because the mold has no side core pulling (the die casting has no side holes and undercuts). Therefore, F lock ≥ KF main=1.25×1288.352=1610.44kN According to the above calculation, the value of clamping force and the weight of the casting are obtained. According to these two main factors, the die-casting machine is selected, and the final selected model is: horizontal cold-chamber die-casting machine (2500kN)————J1125 type, main parameters: ①Maximum metal pouring amount————3.2Kg, ②Mold thickness————250~650mm, ③Moving mold seat plate stroke————400mm, ④Injection force—— —143~280kN.
2.2 Die-casting pressure Die-casting pressure is one of the main parameters in the die-casting process. Therefore, it is of great significance to grasp the pressure change of liquid metal during the die-casting process, and to reasonably control the pressure at each stage of the die-casting process: ① Obtain qualified castings—— —Dense organization, clear outline; ②Initial calculation of specific injection pressure — Calculated according to the selected injection force. The injection specific pressure is also related to the mold cavity space, the wall thickness of the casting, the molten metal process and other factors. Combining the specific parameters of the designed mold and the initial calculation value, the injection specific pressure of the die-casting mold is finally set to 90MPa.
2.3 Die-casting speed The choice of die-casting speed has the following two aspects: injection speed selection and filling speed selection. The choice of the two speeds is very important, which directly determines the internal and external quality and contour definition of the casting. Factors to be considered when selecting the filling speed: ①The size of the casting, ②The complexity of the structure of the casting, ③The type of alloy selected for the casting, ④The level of injection pressure. Specific choices: ①The casting is easier to fill — castings with simple wall thickness or higher internal quality requirements. Choose: low speed, high specific pressure, large gate; ②Fast filling is required —complex thin-walled or For castings with higher surface quality requirements, choose: high speed, high specific pressure. Comprehensive consideration, according to the specific characteristics of the die castings-the structure is relatively simple, select the medium speed, the range is 20 ~ 90m/s.
2.4 Die-casting time determines the die-casting time, which is composed of three parts of the required time: filling time, holding time and the time that the die-casting part stays in the die-casting mold. Several factors combined to produce this result: pressure, speed, temperature, characteristics of molten metal, as well as casting structure (mainly wall thickness and volume) and mold structure (especially the gating system and drain system) and other factors. The filling time is mostly between 0.01 and 0.2s. The length is determined by the size of the casting and the complexity of the structure: a casting with a simple structure and a large volume requires a relatively long filling time; a casting with a more complex structure and a smaller wall thickness requires a short time. Through practical tests, the filling time is set at about 0.2s, which is reasonable for the medium and small aluminum alloy die castings designed in this paper. The function of holding pressure time is: the injection punch has enough time to apply pressure to the unsolidified metal, so that the crystallization process can be carried out under pressure, which enhances the feeding and successfully obtains a dense structure. Factors affecting the length of time: the melting point of the selected alloy, the crystallization temperature range and the wall thickness of the casting. Castings with high melting point, large range and large wall thickness require a long time, 2~3s; when the determined time is too short, shrinkage will appear, but it does not have a significant effect if the holding time is prolonged. 1~2s is the general holding time range. In this design, the average wall thickness of the casting is 3mm. Considering its structure and alloy properties, 3s is selected as the holding time. 2.5 Die-casting temperature The main process parameters to ensure qualified castings — the pouring temperature of the molten metal and the working temperature of the mold. There are many factors that affect it: the structure of the casting, wall thickness, filling pressure, speed and alloy type. It is necessary to comprehensively consider the above parameters to ensure that the die-casting temperature is stable within a reasonable range and provide good filling conditions. If the pouring temperature is not within a reasonable range, the quality of the product will be degraded or even unqualified: ①Excessive pouring temperature — will cause excessive shrinkage during cooling, the product is prone to cracks, larger grains, and poor mechanics Performance, and even cause mold sticking, reduce mold life; ② Too low pouring temperature-cause defects including cold barrier, surface pattern and insufficient pouring. In order to obtain qualified castings, in addition to the pouring temperature, pressure, die-casting mold temperature, filling speed, and the alloy selected for the casting should also be considered at the same time. This die-casting part is made of aluminum-silicon alloy. According to its fluidity and mold characteristics, 620℃ is selected as the die-casting temperature.
Design of Die Structure for Die Casting Parts of Back Shell
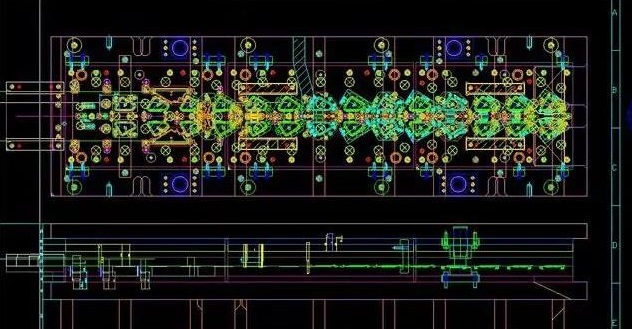
3.1 Determination of Parting Surface The part has a simple structure. According to the principle of parting surface selection, the largest projected section should be selected, as shown in Figure 2.
3.2 Design of the gating system The gating system consists of four parts: ① straight runner, ② horizontal runner, ③ internal gate, ④ cold slug hole. Specific design: ①Integral pressure chamber—the connection method of pressure chamber and sprue sleeve; ②cross-section shape of runner—flat trapezoid; ③inner gate—ring-shaped side gate; ④side pouring Mouth-arranged on the parting surface of the casting; ⑤ One mold with four cavities, Figure 3 shows the specific structure.
3.3 Design of overflow tank and exhaust system The structural design of the overflow tank is carried out, and the cross-sectional shape selected by comprehensive consideration of various factors is trapezoidal (Figure 4). Reasonable structure has the following functions: ①Improve the thermal balance of the mold-adjust the temperature of the mold everywhere, reduce the flow marks, cold barriers and insufficient pouring of the castings, transfer shrinkage cavities, shrinkage porosity, and vortex entrapment; ② discharge The gas in the cavity is quickly exhausted with the exhaust groove; ③storage of cold dirty metal liquid-a mixture of paint residue and gas.
3.4 Design of the ejection system In the die-casting process, after a complete forming cycle is completed, the die-casting part needs to be opened, and the wrapped die-casting part will be found on the side of the punch, which needs to be removed. This task requires an additional one Kind of top piece mechanism to perform. The ejector system occupies an important position in the mold structure design. There are three main parts of the ejector system: ① eject, ② reset, and ③ guide. This set of molds adopts two ejector ejection mechanisms, which are used for casting ejection and runner ejection respectively. The diameters of ejector pins are 6mm and 8mm respectively. Design limit devices in the system: ① limit block, ② reset lever to improve the reset accuracy of the mechanism and prevent the stroke from exceeding the limit during the movement of the mechanism components.
3.5 Calculation of the size of formed parts
3.5.1 Cavity and core size:
3.5.2 Calculate the center distance and position size: where: L-the center distance of the forming part and the average size of the position (mm); L-the average size of the die casting center distance and the position (mm).
3.6 The design of the cooling system chooses an efficient and easy-to-control mold cooling method—water cooling to obtain high-quality castings and long mold life. The cooling effect of water cooling depends on the layout of the cooling channel, which is arranged in the cavity: ①The highest temperature, ②The heat is more concentrated, ③Under the mold, ④The side opposite the operator. In order to improve the installation convenience of the water delivery hose, it is required to unify the geometrical dimensions of the outer diameter of the water channel. Its structural arrangement is shown in Figure 5.
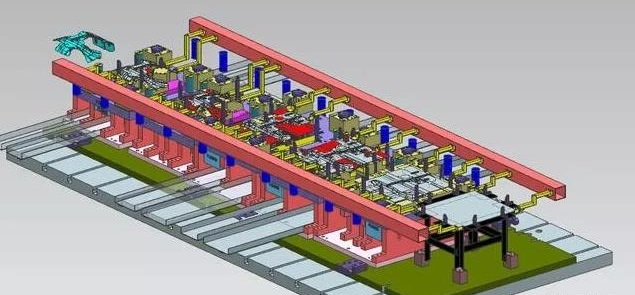
3.7 General Assembly Drawing of Die-casting Mould Make the general assembly drawing of the die-casting mould of the back shell cover (Figure 6). The die-casting mold is composed of two parts: a fixed mold and a movable mold. The fixed mold is stationary and is located on the fixed mold plate. The movable mold moves with the follower plate and is located on the follower mold fixed plate. The mold clamping and mold opening are realized by the movement of the movable mold relative to the movable mold. ① Mold clamping: the two are closed to form a cavity, and the cavity is filled with molten metal under high pressure using a gating system; ② mold opening: the two are separated after the pressure is maintained, and the ejection mechanism completes the task of ejecting the product from the cavity.
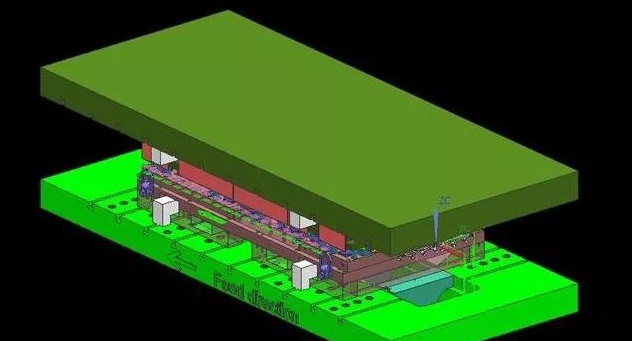
We uses UG software to model the back cover parts, and completes the manufacturability analysis, die casting process parameters and mold structure design of the back cover parts. The cavity is limited by the following factors: manufacturing, process and production Efficiency, etc., considering the above factors comprehensively, it is determined to be a more reasonable one-mold four-cavity layout. Practical production shows that the die-casting specific pressure of 90MPa is selected, the die-casting speed is selected in the range of 20-90m/s, the casting time of 0.2s, the holding time of 3s, and the die-casting temperature of 620℃, the resulting back shell stuffy cover It has a smooth surface and meets product quality requirements.






