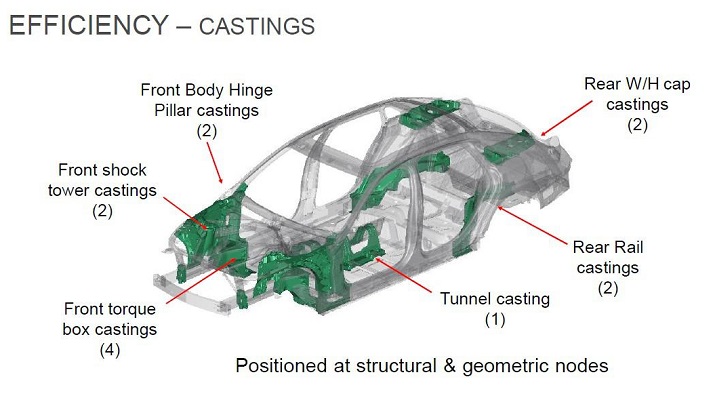
Aluminum alloy car body die-casting structural parts
I. Overview
Before the launch of Tesla’s new energy vehicles in the United States, the Stuttgart Automotive R&D Center in Germany and Rheinland Corporation conducted effective research and development on the materials and processes of aluminum alloy die-casting structural parts, and they have been applied in related models.
The introduction of new energy vehicles has led to a revolution to traditional fuel vehicles, and heralded the prospect of intelligent vehicles………, and the introduction of body die-casting structural parts will further expand the application space of aluminum alloy die-casting products. Lightweight cars will have a profound impact.
In the transformation from traditional fuel vehicles to new energy vehicles, the body structure adopts aluminum alloy die-casting. The overall structure is compact, the rigidity is increased, and the weight is reduced. These advantages are reflected. However, to achieve this technological transformation and change, many technical elements Still need to analyze and discuss carefully.
2. Control elements of die-casting structural parts of car body
1. The coordination of the product design drawing of the car body structure and the die-casting casting drawing. The selection of alloy materials involved in the product drawing is related to the casting process and its reasonable feasibility. According to the ASTM B85 aluminum alloy technical standard, the die-casting characteristics of the die-casting alloy should be carried out. Assess, the stress load areas of important parts of the structural parts should be clearly marked in order to provide a basis for the inspection of die-casting samples to ensure the quality of the structural parts. These are rare in the past by conventional aluminum alloy die-casting.
2. Design and manufacture of die-casting mold for structural parts, design of pouring system and analysis of mold flow
The process design of the die-casting mold, the design of the pouring system, the thermal balance layout of the mold cooling and heating system, and the design of key gate sections and proportions should be reasonable and feasible, and ensure the quality of the high stress area of the product, and appropriate if necessary Improve the tonnage of the clamping force of the press according to the projection area and the vacuum die-casting capacity.
3. Alloy selection of die-casting structural parts
The high plasticity requirement of general mechanical properties of die-casting structural parts is a prominent feature, and the selection of alloy chemical composition should consider both performance and the forming requirements of die-casting parts and the uniformity of wall thickness. The alloy material selection work for die-casting structural parts in Europe is roughly summarized. For the following table:
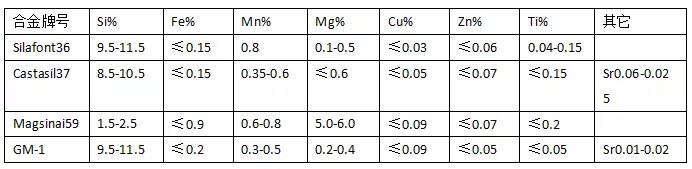
The mechanical performance requirements: tensile strength ≥250Mpa, elongation ≥10%, according to the performance requirements, combined with the chemical composition of GM-1 and the structural features of its product drawings, a multi-component trial production test was carried out in batches. . The choice of silicon element close to the eutectic composition is to meet the molding needs of the thin wall and complex shape of the die-casting product. Another feature of adding silicon is that the recent microscopic research and analysis show that the silicon element expands during the solidification process of the casting, which reduces It shrinks and balances the tendency of thermal cracking with other elements, which also suppresses the casting stress to a certain extent. However, the silicon element reduces the solubility of hydrogen in the liquid alloy, so that the hole defects of the silicon-containing alloy with high silicon content, especially close to the eutectic composition, are the biggest drawbacks. Strict control of iron content is necessary for high plastic properties. As for the sticking problem of die castings, the addition of appropriate manganese can play a similar role. The following is a schematic diagram of the metallographic diagrams of the various elements, and their role in the alloy is interpreted. For die-cast aluminum alloys, the addition of Cu or Mg is the usual matrix strengthening element, that is, the corresponding Al2Cu or Mg2Si strengthening phase is formed through the die-casting process The chilling in the medium makes it partly solid solution strengthened, and the T1 aging treatment is used for the die casting, which also produces precipitation hardening on the solid solution part to achieve performance improvement.

Figure 1: Typical void defects of eutectic AL-SI alloys

Figure 2: AL3Fe\AL6Mn compound in die-cast aluminum alloy
Although the high-speed cooling rate of high-plasticity die-casting aluminum alloy can inhibit the growth of AL3Fe, its acicular structure is fatal to high plasticity. Therefore, it is proved to be effective and feasible to replace iron with AL and Mn compounds formed by adding Mn to form squares.
The long-lasting effect of strontium and the modification of die-casting eutectic Al-Si alloys are effective. Although it has a tendency to absorb hydrogen, it can be solved in the strengthening and purification process of the alloy.
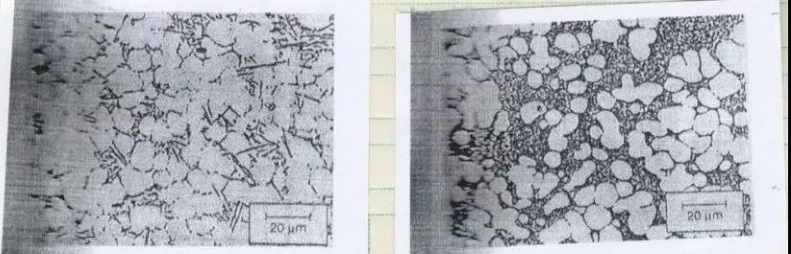
Figure 3: Comparison of the deterioration effect of strontium
It can be seen from the modification effect of strontium in Fig. 3 that the morphology of eutectic silicon after this modification is desirable for high plasticity.
4. Alloy melting and purification
Due to the mechanical properties of car body die-casting structural parts, it must be realized by heat treatment. The heat treatment of die-casting parts, especially solution treatment, has special requirements for alloy purification and vacuum die-casting, so the car body structure Alloy liquid treatment requires both degassing and slag removal, and flux treatment is required when necessary. The test shows that the slag inclusion of AL2O3 in the aluminum liquid has a strong adsorption effect on the hydrogen in the refining, and will form an adsorption core, making it difficult to remove. The purpose of the purification treatment is to take into account its dual functions. The following figure shows the time of the purification treatment. It’s effective.
5. Vacuum die casting
In view of the special requirements for the performance of the car body structure and the structural characteristics of the die-casting parts, vacuum die-casting is generally used for the car body structural parts, and the use of a dedicated vacuum die-casting machine has proved to be the best choice, such as the German Fulai vacuum die-casting machine The response is good. The vacuum die casting machine can hydraulically cast the purified alloy into a basically defect-free product. Of course, the optimization of the parameters, the preparation of the mold design and manufacturing, and the coating spraying must be adapted to it. The quality of vacuum die castings is closely related to the final performance of heat treatment. The tonnage of the clamping force of the die casting machine can be optimized according to the importance of the car body structure. If necessary, the model with a higher level can be selected according to the general projection area. Ensure the quality and safety of structural parts.
6. Heat treatment
For the heat treatment of aluminum alloy car body structural parts, the information known so far shows that solution treatment and high temperature aging are generally used at home and abroad, that is, T7 treatment. The national military standard GJB1695 cast aluminum alloy heat treatment specification edited by the author is for T7 The heat treatment specifications are specifically listed. It is approved and issued by the National Defense Science and Industry Commission and verified by many companies in the national aviation industry. We have also been recognized in discussions and communication with the chief metallurgist of GM. The high plasticity of the alloy is feasible.
It should be pointed out that the determination of the solution treatment and high temperature aging specifications depends on the alloy composition and the specific conditions of the die casting, including the temperature and holding time of the treatment. The specific specifications can refer to the relevant alloy series of GJB1695. In summary, the analysis of the control elements of the car body die-casting structural parts involves a lot of process points. It is only a summary of the practice, and it is difficult to give a complete overview. Many arguments are still worthy of discussion and further verification.
3. Discussion
1. Die-casting structural parts of the car body replace part of the original deformed aluminum profile plates, and more are stamped parts, riveted and welded parts. Although the overall structure of the car body is compact, the rigidity and weight reduction have obvious advantages, but from the structural parts The design safety factor, service life and comprehensive measurement of existing die-casting operation methods are still perfect. In particular, how to prevent the accidental quality of die-casting parts and the instability of internal quality before it is worthy of further investigation.
2. Establish and improve related inspection methods for car body die-casting structural parts, including refinement and intensification of existing conventional methods, especially through regular sampling inspections, design and performance testing of cut samples at designated locations, and through stable process and process control. Achieve stable quality of die castings, etc.
3. Strictly evaluate the trial production and finalization of aluminum alloy structural parts, design and process evaluation, and implement a countersignature system for key structural parts when necessary. This has more successful precedents and mature experience in the aviation industry for reference.
4. For foreign trade related die-casting structural parts, the corresponding inspection level can be improved according to the quality requirements of customers, and the conditions are not sufficient to create conditions, external promotion and internal promotion, and improve the quality of die-casting parts to meet the needs of the foreign trade market.
5. It is feasible to implement an enterprise-centered R&D system combining production, school and research, especially when the R&D strength of the enterprise is weak.
6. Recently, regarding the question of whether strengthening elements in eutectic Al-Si alloys can be superimposed, the author’s opinion is: in terms of the current application status of die-casting aluminum alloys at home and abroad, in addition to eutectic Al-Si alloys In addition, hypereutectic AL-Si alloys such as 390 in the United States or ADC14 in Japan and YL-117 in China have the common feature of adding the strengthening elements Cu and Mg at the same time. This is based on the hypereutectic Si. The eutectic structure can contain the coexistence of its strengthening phases, but for this type of alloy, there must be corresponding means of adding phosphorus to modify, and corresponding casting process control measures to prevent the appearance of coarse primary Si and cause difficulties in machining.